It’s not easy to create DEM in areas where there is thick vegetation. Manpower is not realistic, photogrammetry is not capable for this job and big Lidar with manned aircraft is a good method but too pricy. UAV Lidar provides a feasible and affordable solution.
We hereby introduce a case study of mapping thick vegetation mountain area using UAV Lidar GLV.
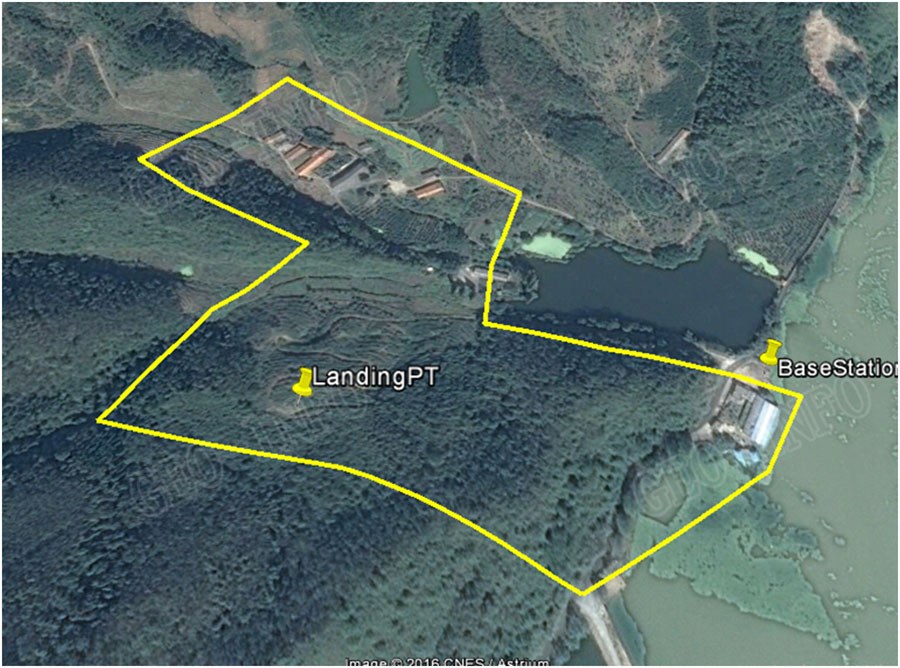
1、Basic information about the project:
To create 1:2000 scale DEM for the yellow line area, using UAV Lidar GLV.
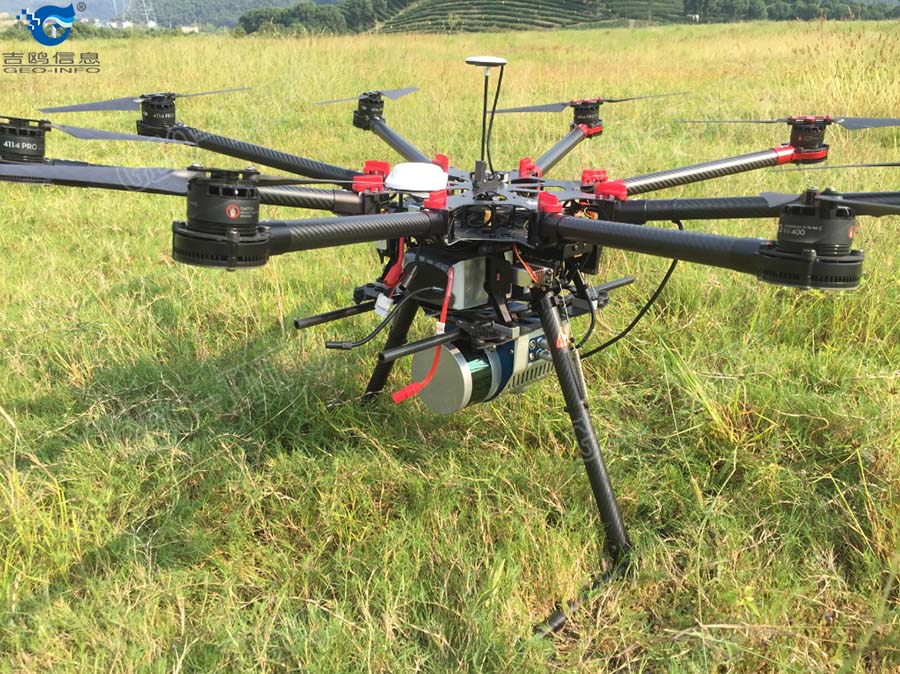
2、System preparation:GLV mini Lidar + DJI’s S-1000 octocopter

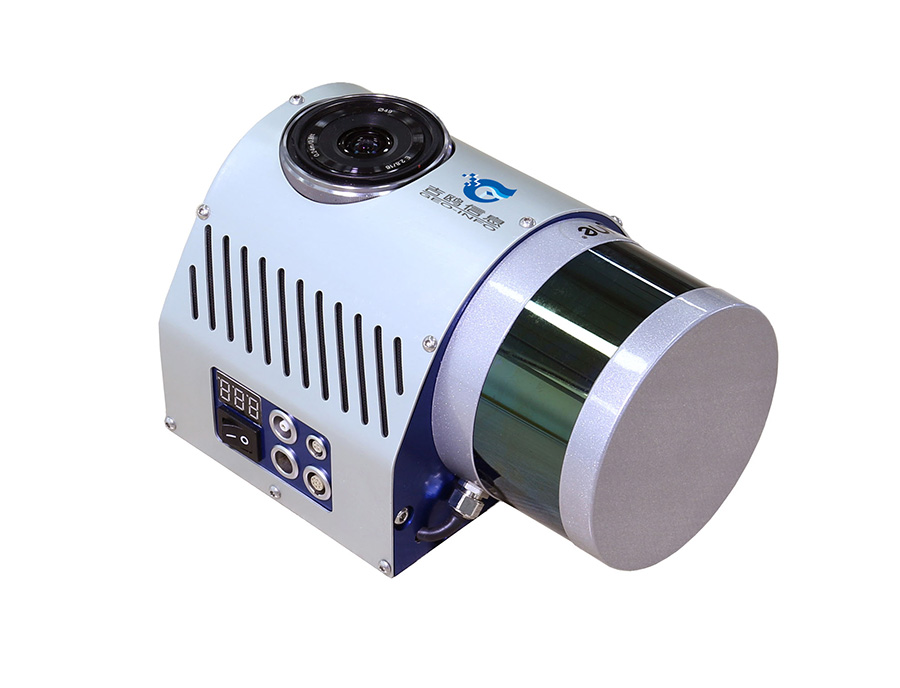
GLV technical specs:

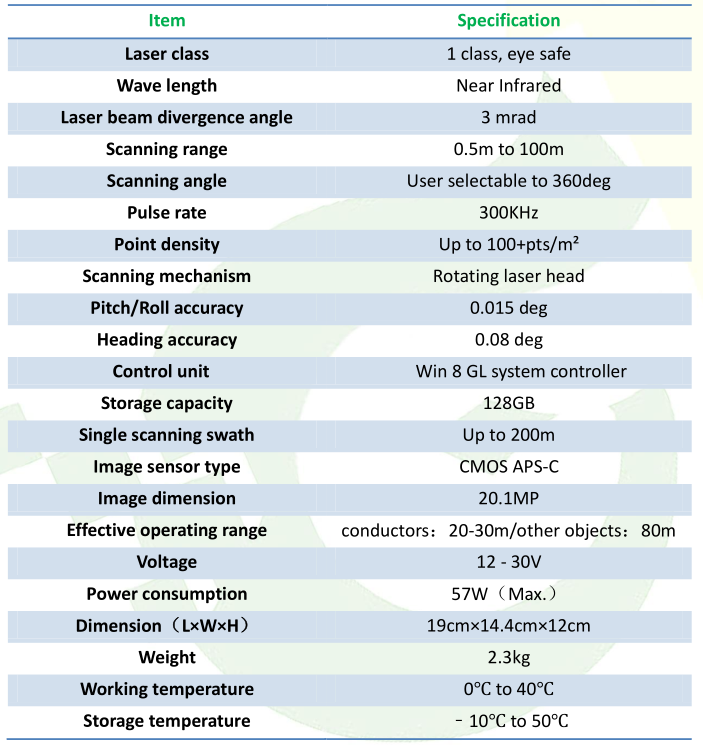
3、Flight lines design and flying on site:
After onsite check, the project team from Geo-info picked a flat spot half way on the hill as landing site and designed flightlines according to the technical specs of both GLV and S-1000. 2 missions were flown and the total flying time was 22 minutes.
![1481696966948925VIm7.jpg D~[W(4XKVT]ZX25`3GKI3HQ.jpg](http://www.geo-info.cn/en/upload/at/image/20161214/1481696966948925VIm7.jpg)
4、Onsite flying pictures:
![1481696975582329sjz3.jpg P%JRURS[{LJ$$7B]H8~I_99.jpg](http://www.geo-info.cn/en/upload/at/image/20161214/1481696975582329sjz3.jpg)
5、Data display:
At the completion of flying, Geo-info team rapidly processed data using Geo-LAS software to check for coverage. And data post-processing was conducted afterwards to create DEM, shown as below.
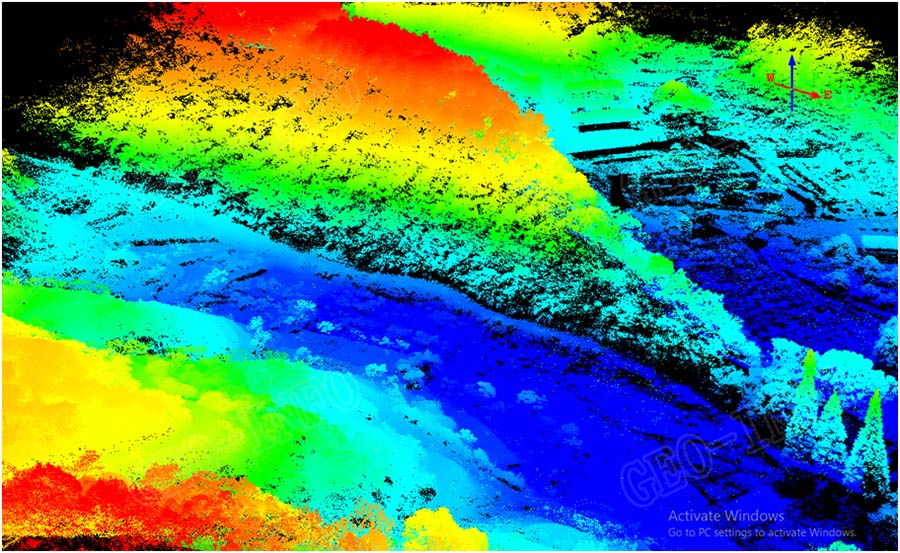
DSM was then further processed with laser point classification to generate DEM, as shown below. As we can see from the picture, mountain shapes and the ridges are clearly defined with laser points, which proved the vegetation penetration ability of GLV Lidar system.
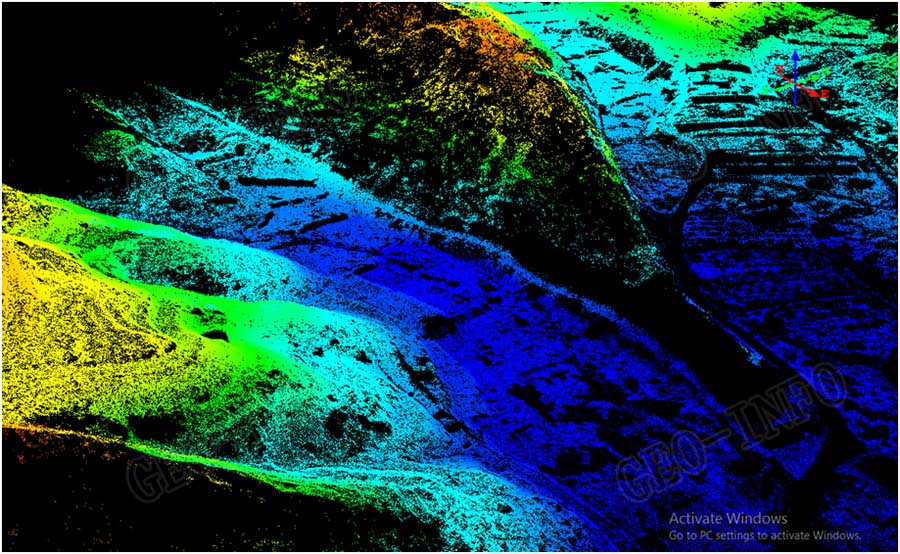
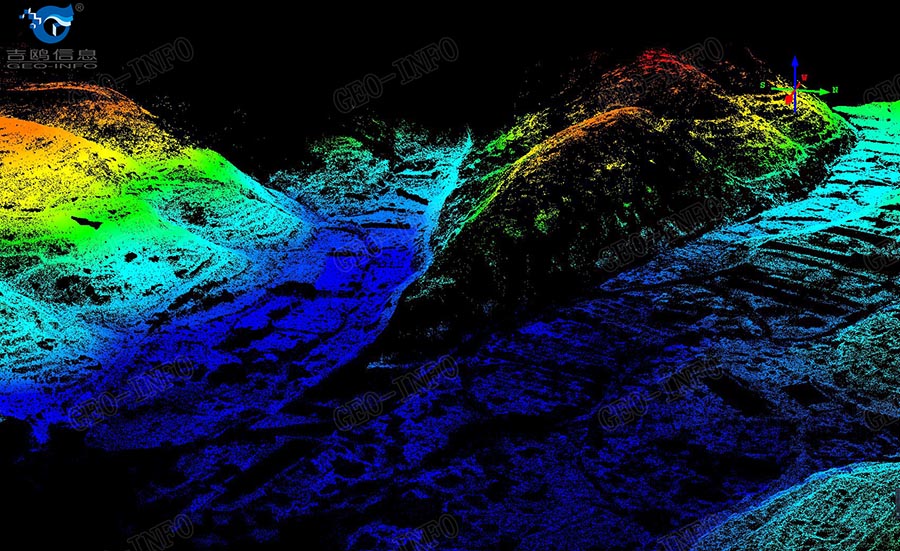
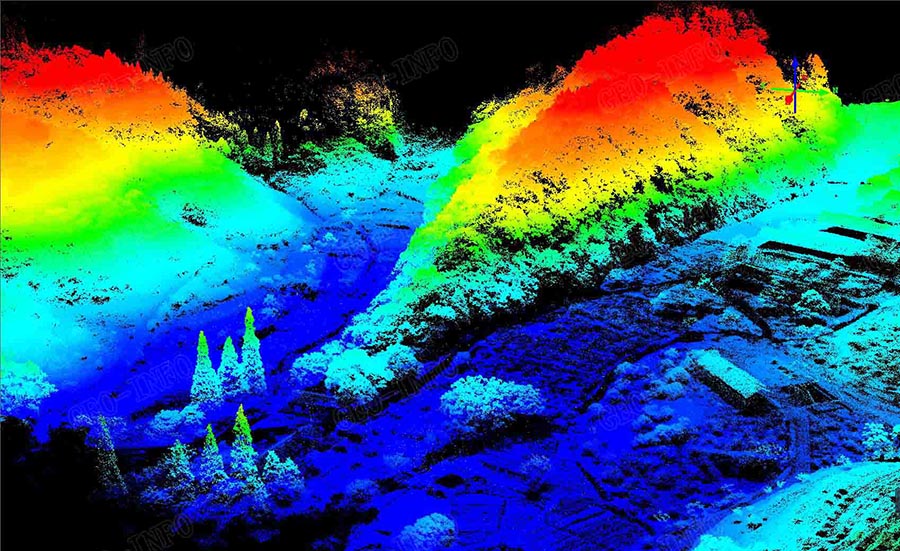
A shaded relief picture shown below was generated after auto filtering of the laser data, all the details of the terrain in this area were clearly defined.

Images of the area were captured simultaneously, to define the objects on the ground, to generate DOM rapidly using Geo-info’s data process workflow, and/or to attribute RGB value to the laser points.
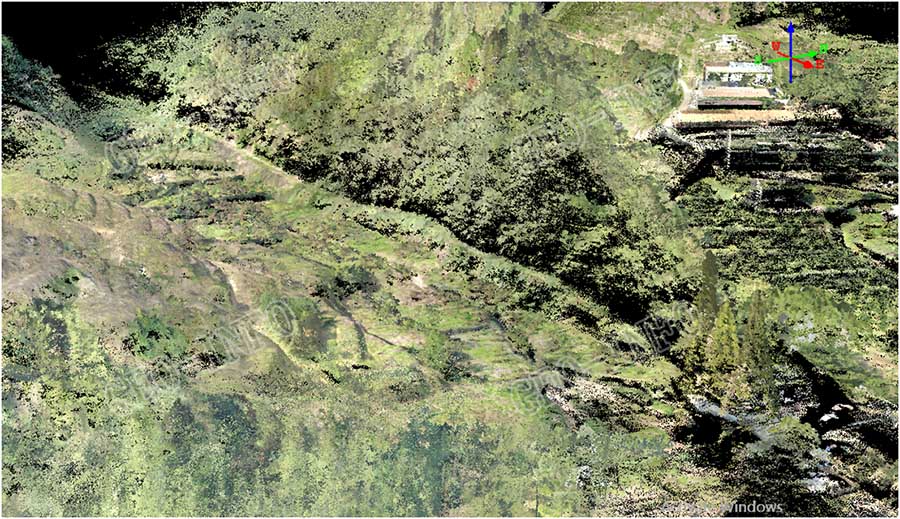
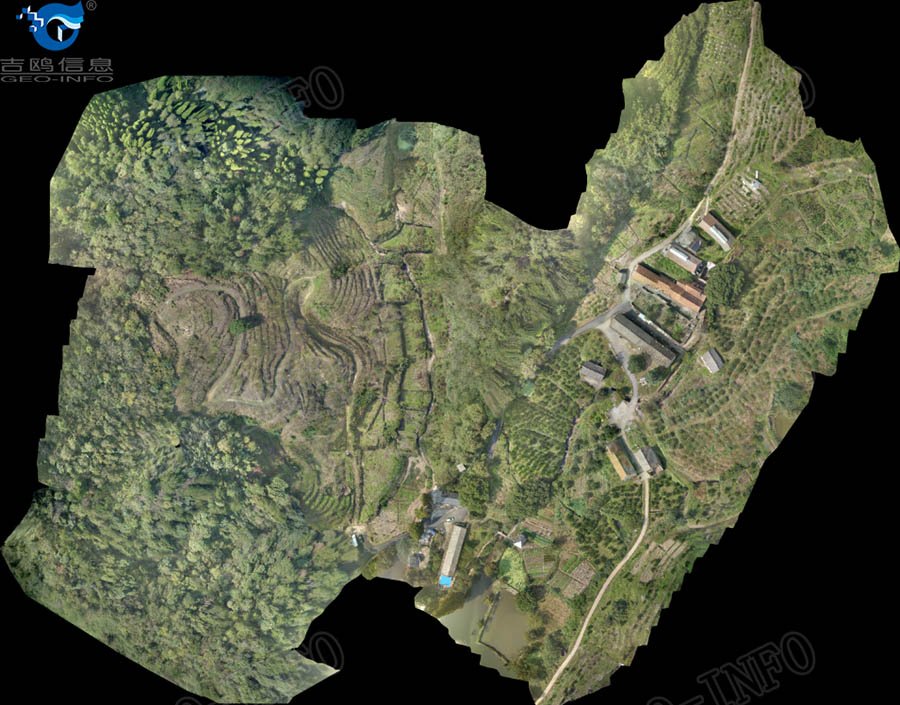

6、Coordinates conversion and accuracy check by customer:
GLV Lidar system generates data in WGS84 coordinates system. However, most projects are delivered in customer-defined coordinates systems. Therefore, the last step is coordinates conversion. Given our expertise in mapping industry, this last step was done rapidly and accuracy check was conducted with great satisfaction.
Conclusion:
This case study proves that GLV is totally capable of mapping small hill areas with thick vegetation to generate high accuracy DEM.
The disadvantage of this solution is that the efficiency was low due to short range of the scanner and the short flying time. It can be used to map small areas or to patch holes for big area mapping at thick vegetation areas.
Ways to improve:
1) Change flying platform to gain longer flying time
2) Use GL-70/70A with Dragon 50, with range more than 700 meters and flying time up to 2 hours.






